| 出品公司: | SBI |
|---|---|
| 载体名称: | pCDH-EF1-MCS-(PGK-Puro) |
| 质粒类型: | 慢病毒表达载体;cDNA表达载体;双向启动子载体 |
| 克隆方法: | 多克隆位点,限制性内切酶 |
| 启动子: | EF1a |
| 载体大小: | -- |
| 5' 测序引物及序列: | EF1-F :5’-CTCCACGCTTTGCCTGACCCTGCTT-3’ |
| 3' 测序引物及序列: | -- |
| 载体标签: | 无 |
| 载体抗性: | 氨苄青霉素(Ampicillin) |
| 筛选标记: | 嘌呤霉素 |
| 克隆菌株: | E.coli cells(RecA-)推荐: Stbl3 ,OmniMAX 2 T1R |
| 宿主细胞(系): | 在大多数类型的细胞高效表达,包括原代细胞,分化细胞,干细胞 |
| 备注: |
pCDH-EF1-MCS-(PGK-Puro)载体是基于HIV的慢病毒载体; 用于cDNA表达和克隆;高效转染细胞,建立稳定细胞系; EF1a启动子驱动目 的基因的中等水平表达,PGK启动子驱动报告基因的高水平的表达。 |
| 产品目录号: | CD810A-1 |
| 稳定性: | 稳表达 |
| 组成型/诱导型: | 组成型 |
| 病毒/非病毒: | 慢病毒(HIV) |
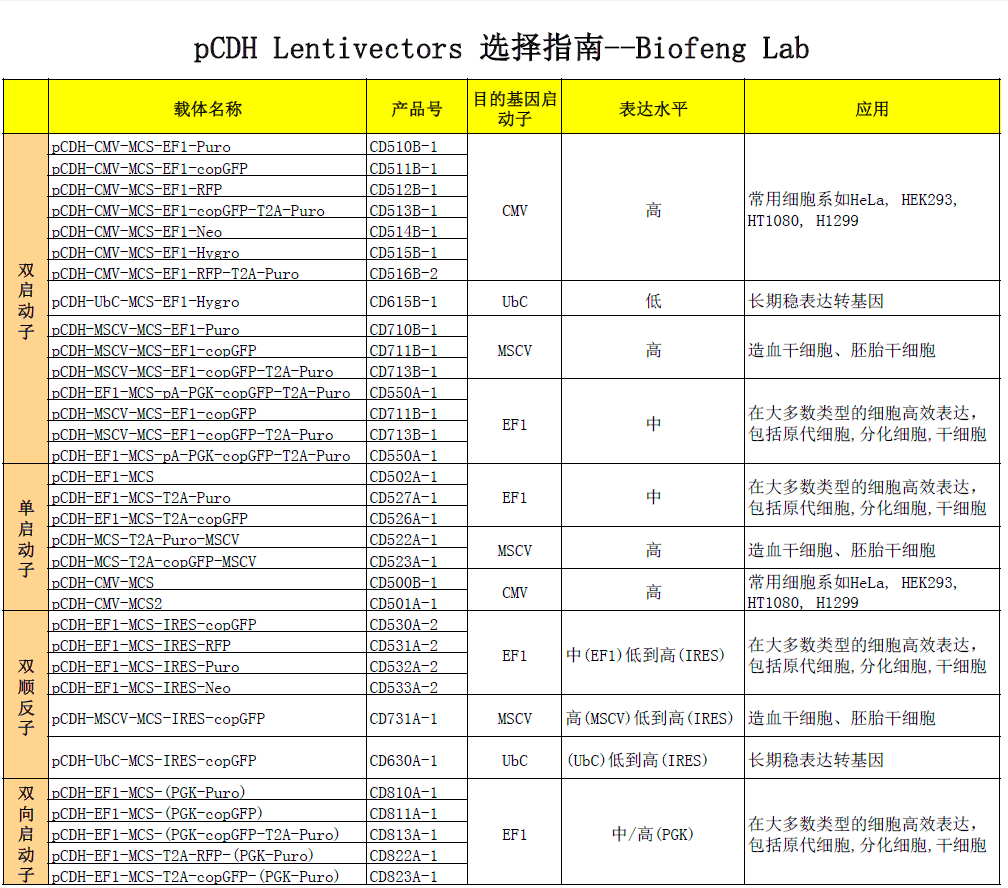
买家导航

pCDH-EF1-MCS-(PGK-Puro)载体质粒基本信息
pCDH-EF1-MCS-(PGK-Puro)质粒图谱载体图谱和pCDH-EF1-MCS-(PGK-Puro)载体序列质粒序列多克隆位点信息
 载体图谱.jpg)
pCDH-EF1-MCS-(PGK-Puro)质粒载体简介
背景简介: This manual provides details and information necessary to generate expression constructs of your gene of interest in the pCDH cDNA Cloning and Expression Lentivectors. Specifically, it provides critical instructions on amplification and cloning cDNA into the pCDH vectors, and verification of the final expression constructs. This manual does not include information on packaging the pCDH expression constructs into pseudotyped viral particles or transducing your target cells of choice with these particles. This information is available in the user manual Lentivector Expression Systems: Guide to Packaging and Transduction of Target Cells which is available on the SBI website. Before using the reagents and material supplied with this system, please read the entire manual. 基于HIV-1的pCDH 慢病毒载体特征: Multiple Cloning Site (MCS)—for cloning the gene of interest in the MCS located downstream of the CMV promoter. WPRE element—enhances stability and translation of the CMV-driven transcripts. SV40 polyadenylation signal—enables efficient termination of transcription and processing of recombinant transcripts. Hybrid RSV/5LTR promoter—provides a high level of expression of the full-length viral transcript in producer 293 cells. Genetic elements (cPPT, gag, env, LTRs)—necessary for packaging, transducing, and stably integrating the vira expression construct into genomic DNA. SV40 origin—for stable propagation of the pCDH plasmid in mammalian cells. pUC origin—for high copy replication and maintenance of the plasmid in E.coli cells. Ampicillin resistance gene—for selection in E.coli cells. pCDH 慢病毒表达载体的优势: Lentiviral expression vectors are the most effective vehicles for the delivery and expression of a gene of interest to almost any mammalian cell—including non-dividing cells and model organisms (C.A. Machida, 2003; M. Federico, 2003; W. C. Heiser, 2004). As with standard plasmid vectors, it is possible to introduce lentivector expression constructs in plasmid form into the cells with low-to-medium efficiency using conventional transfection protocols. However, by packaging the lentivector construct into viral particles, you can obtain highly efficient transduction of expression constructs—even with the most difficult to transfect cells, such as primary, stem, and differentiated cells. The expression construct transduced in target cells is integrated into genomic DNA and provides stable, long-term expression of the target gene. pCDH 慢病毒载体的包装载体及细胞系 The expression lentivector contains the genetic elements responsible for packaging, transduction, stable integration of the viral expression construct into genomic DNA, and expression of the target gene sequence. The packaging vector provides all the proteins essential for transcription and packaging of an RNA copy of the expression construct into recombinant viral particles. To produce a high titer of viral particles, expression and packaging vectors are transiently co-transfected into producer mammalian cells (e.g., HEK 293 cells). For a detailed description of SBI’s Lentivector expression system,please refer to the Lentivector Expression System user manual. 启动子的选择: SBI provides a collection of cDNA cloning and expression vectors for various applications. A gene of interest can be cloned under a CMV or EF1 promoter with or without another expression cassette for a reporter gene (copGFP or PuroR). Genes can be either expressed transiently through transfection or stably expressed in a target cell line through transduction with packaged viral particles. The major concern of cDNA expression in lentivectors is the efficiency level and stability of expression in target cell lines. The Cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter is a strong and most commonly used viral promoter that constitutively expresses downstream genes. While the CMV promoter works perfectly in the most common cell lines, it shows poor expression in some stem cell lines and hematopoietic cell lines (R.F. Doll, 1996; E.D. Papadakis, 2004). The housekeeping elongation factor 1α (EF1) promoter has been shown to exceed and outlast CMV-mediated expression in retroviral, lentiviral, and adenoviral vectors, in hematopoietic cell lines (K. Tokushige 1997; H. Nakai, 1998; C. Teschendorf, 2002). EF1 also performs well in most common cell lines. MSCV promoter is the 5’-LTR promoter of murine stem cell virus. When a portion of the U3 region of the 3’ HIV LTR was replaced with the U3 region of MSCV LTR, the resulted hybrid HIV/MSCV LTR has dramatically increased the transgene expression level in human CD34+ hematopoietic cells (J.K. Choi, 2001). After integration into genomic DNA, this promoter transcribes a long transcript with an intron in the 5’UTR flanked with splice donor and acceptor sites derived from the lentiviral vector. Further studies found that additional CpG mutations in the MSCV LTR reduced transcriptional silencing in embryonic stem cells (C.S. Swindle, 2004). We constructed cDNA expression vectors with the CpG-deficient MSCV incorporated into the 3’ HIV LTR. After integration into genomic DNA, 3’MSCV/LTR will replace the 5’LTR and provide a high level of expression of the target gene and reporter gene downstream. 1.单启动子载体 These lentivectors are characterized by the presence of a single mammalian promoter driving the gene on interest cloned into the MCS, either expressed by itself or co-expressed with a marker gene of interest (e.g. copGFP or Puro) in a T2A format 2.双启动子载体 These lentivectors are characterized by the presence of two independent mammalian promoters, one driving the gene of interest cloned into the MCS and the other driving the expression of a marker (e.g. copGFP, Puro, or GFP-T2A-Puro). Since the gene of interest and the marker(s) are driven independently, their expression may differ depending on promoter activity. These vectors are typically used to assess transduction efficiency or generate stably selected cell lines independent of the gene of interest 3.双顺反子载体 Bicistronic vectors are vectors that generate multiple, native proteins from a single mRNA transcript. It is useful for applications where coupled transcription of a gene of interest with a marker (e.g. GFP) under the control of a single promoter is desired. One well-characterized approach for bicistronic vectors is the use of an Internal Ribosomal Entry Site (IRES) element (Jang 1988) which allows for translation of a marker gene of interest anywhere in the mRNA transcript by recruiting ribosomes to IRES sites to initiate translation in a cap-independent manner. 4.双向启动子载体 Express multiple transgenes simultaneously SBI has built and tested a suite of synthetic bidirectional promoter lentivector formats featuring EF1a and PGK in a divergent configuration coordinating the regulation of two or more different transgenes. This promoter configuration takes advantage of the natural bidirectional activity of the PGK promoter and the divergent configuration is stable and resistant to silencing in embryonic stem (ES), trophectoderm stem (TS) and extra embryonic endoderm (XEN) stem cells (MC Golding and MRW Mann, 2011). The primary benefits of these formats are that researchers can coordinate dual expression of their genes of interest as well as various markers (GFP, RFP, Puro, etc.) without the use of IRES elements which have weak functions when co-expressing two cDNAs and can avoid unidirectional promoter interference issues that sometimes arise in lentivector formats. Divergently transcribed genes contribute to more than 10% of the human genome. This signifies that the bidirectional promoters are very prevalent and these promoters are responsible for coordinated expression of genes in the cell (Adachi et al. 2002, Golding et al. 2011). Coordinated expression of more than one transgene is very important for studying gene or non-coding RNA function and regulation or in gene therapy (Kay et al. 2001). IRES based vectors or bicistronic vectors offer that opportunity, however it has been sown that the second gene in the IRES based vector gets compromised by the expression of the first gene (Mizuguchi et al. 2000) and promoter interference is often a factor in bicistronic vectors (Curtin et al. 2008, Callen et al. 2004). Self cleaving peptides are routinely used to express two or more transgene but it has been shown that these peptides can sometimes affect protein function and stability. SBI offers a synthetic bi-directional promoter with EF1 and PGK in a divergent configuration coordinating the regulation of two or more different transgenes. This promoter configuration takes advantage of the natural bidirectional activity of the PGK promoter and the divergent configuration is stable and resistant to silencing in embryonic stem (ES), trophectoderm stem (TS) and extraembryonic endoderm (XEN) stem cells (Shin et al. 2006, Stegmeier et al. 2005, Golding et al. 2011).The multiple cloning site (MCS) in the positive orientation of the bi-directional promoter which allows for convenient cloning of your gene or non-coding RNA of interest. The SV40 and BGH polyadenylation signals in both end of the vector enables efficient termination of transcription, resulting in high levels of steady-state expression. In the negative orientation of your expression cassette is the expression of the Puro, copGFP or GFP-T2A-Puromycin marker genes. SBI第三代慢病毒载体 SBI offers a third generation of the most popular HIV-1 based lentivector expression system which consists of three maincomponents: (1) The lentiviral expression vector (e.g., pCDH-EF1-MCS-T2A-Puro) (2) The lentiviral packaging plasmids (e.g., pPACKH1 Packaging Plasmid mix) (3) A pseudoviral particle producer cell line (e.g., 293TN cells) 2A Peptide-enabled dual expression system Coexpression of a reporter gene together with a gene of interest is a useful approach for selecting transfected or transduced cells. This is commonly achieved by using two independent internal promoters, such as CMV and EF1 in pCDH-CMV-MCSEF1- copGFP, or by linking two transgenes with an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) element in a single bicistronic transcript. Many dual promoter pairs have shown a high level of expression of both transgenes in standard cell lines— however, promoter interference often occurs in some cell lines. There are also two main problems that limit the use of IRES: the large size and the imbalanced expression between the first and second cistrons (H. Mizuguchi, 2000; X.Yu, 2003). The “self-cleaving” 2A peptides have been used successfully to generate multiple proteins from a single promoter in many applications (P. de Felipe, 2004; M.J. Osborn, 2005; P. de Felipe, 2006). The 2A-like sequences exist in several viruses and are used to mediate protein cleavage from a single open reading frame. Through a ribosomal skip mechanism, the 2A peptide prevents normal peptide bond formation between the 2A glycine and the 2B proline without affecting the translation of 2B (M.L. Donnelly, 2001):SBI’s cDNA expression vectors incorporate the 2A-like sequence (T2A) from the insect virus Thosea asigna to mediate the coexpression of a reporter gene with the target cDNA. Reporter genes have been cloned at either the first or second positions, and we achieved high expression levels at both locations.